I'm sure you've heard about the PDCA cycle, right? How about the SDCA Cycle, have you also heard or read anything about it? Maybe this term is still unknown to you but in this article you will know the differences between the PDCA and the SDCA.
You will also know what is the current need to use them in parallel, since sometimes this remarkable recommendation ends up being forgotten in the business environment.
What is the difference between SDCA and PDCA?
The PDCA Cycle and the SDCA Cycle are two structured thinking methodologies that have the same common approach: acting on a problem or an opportunity. While the PDCA Cycle seeks to solve a problem as efficiently as possible, the SDCA Cycle seeks to keep the process running with the assurance that this problem will not recur.
As an example, think about when you climb a ladder: to go to the next step you have to rest your feet on the stable surface of the previous step, correct?
The relationship between these two methodologies is the same! To achieve greater performance and competitive advantage through the use of the PDCA Cycle, a company must first support its new goals and objectives based on its current situation and for this, the SDCA Cycle is used.
Understand the main tools of this methodology and know how to apply it with excellence to increase productivity!
With this eBook The main tools of Lean Six Sigma you will understand the concept of Six Sigma, as well as a compilation of the main tools used by Belts in the application of each step of the DMAIC method.
These tools will help you to define, measure, analyze and propose solutions to problems that affect the performance of your company's organizational processes.
In this material, in addition to obtaining the definition of each of these tools, what they are used for, and how to use them, you will also find application tips using the Minitab software. So don't waste your time and download now!
So how does the SDCA cycle work?
Step 'S' within this method represents Standardize. Therefore, the SDCA Cycle has the following steps: Standardize, Do, Check, and Act.
Once better performances have been achieved through the PDCA Cycle, the process or product that suffered the transformation needs to be standardized, correct? Systems and devices that prevent the return of these problems must then be developed and put into practice so that it is indeed possible to control and ensure the permanence and stability of all changes. However, if any solved problem returns, corrective action it is the last option.
Tools such as 5S, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), Control Charts and Statistical Process Control (SEP), Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and Poka-Yoke Devices, can help in this mission.
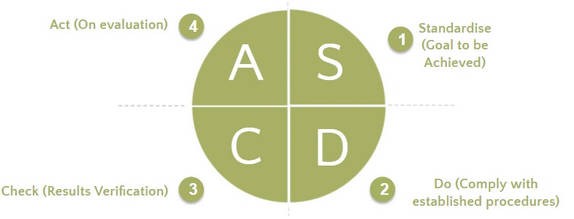
Let’s find out what each step of the SDCA does:
Standardise
The objective of this stage is to define the goal to be achieved, considering the limits of acceptance.
For this, you can define product characteristics, the critical product characteristics (those that have the most impact for the consumer) and define the operational control indicators.
For example: Decrease the amount of scrap to 1 ton per year.
In this step, the SOP (Standard operating procedure) is also defined with the mapping of processes and those who are responsible for executing the SOP.
Do
The objective is to comply with the established procedures.
For that, it is necessary the team training and the provision of the procedures
Check
Check the effectiveness of the previous steps by monitoring the results achieved
Act
The objective of this step is to correct problems that were not previously foreseen
For example: The procedures are not being carried out, the team was unable to understand the goal, the results were not as expected and inadequate working conditions
Why in the industrial environment is it so rare to hear about the SDCA cycle?
Because the application of the SDCA Cycle was, to a certain extent, introduced to the Acting phase of the PDCA Cycle itself, which is the main motive behind having few information about it in industrial and administrative daily life.
While the PDCA Cycle encourages the development of prevention and improvement projects, the SDCA Cycle only alerts you when new problems arise or old ones return, as their purpose is to keep the process operating in a stable and predictable way, without a preventive approach.
The use of an auxiliary method is a condition that DMAIC methodology, for example, does not have, since its own and last phase Control already counts in advance with these warnings and recommendations, assuring the same structured thought of action on a problem and also on the process in which it is inserted.
How important is the parallel use of the PDCA Cycle and the SDCA Cycle?
Regardless of whether a company separates them by name or not, understanding the importance of using these methods in parallel is crucial, as it is not enough to only achieve better results, you must also keep them afterwards! It is only in this way that the actions of correction, prevention and improvement actually perpetuate themselves over time.
I want to learn more about it!
Continue to specialize in the Lean Six Sigma methodology and take the next step for your professional recognition now! With the advancement of tools and techniques from Green Belt to Black Belt you will be able to delve even deeper into this methodology, offer greater results to organizations, consequently being a prominent professional in the market!
|